Mahapadma Nanda on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mahapadma Nanda (
 According to the Puranas, Mahapadma or Mahapadma-pati (literally, "lord of the great lotus") was the first Nanda king. He was the son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a
According to the Puranas, Mahapadma or Mahapadma-pati (literally, "lord of the great lotus") was the first Nanda king. He was the son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during ...
: ''Mahāpadmānanda''; c. mid 4th century BCE), according to the Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
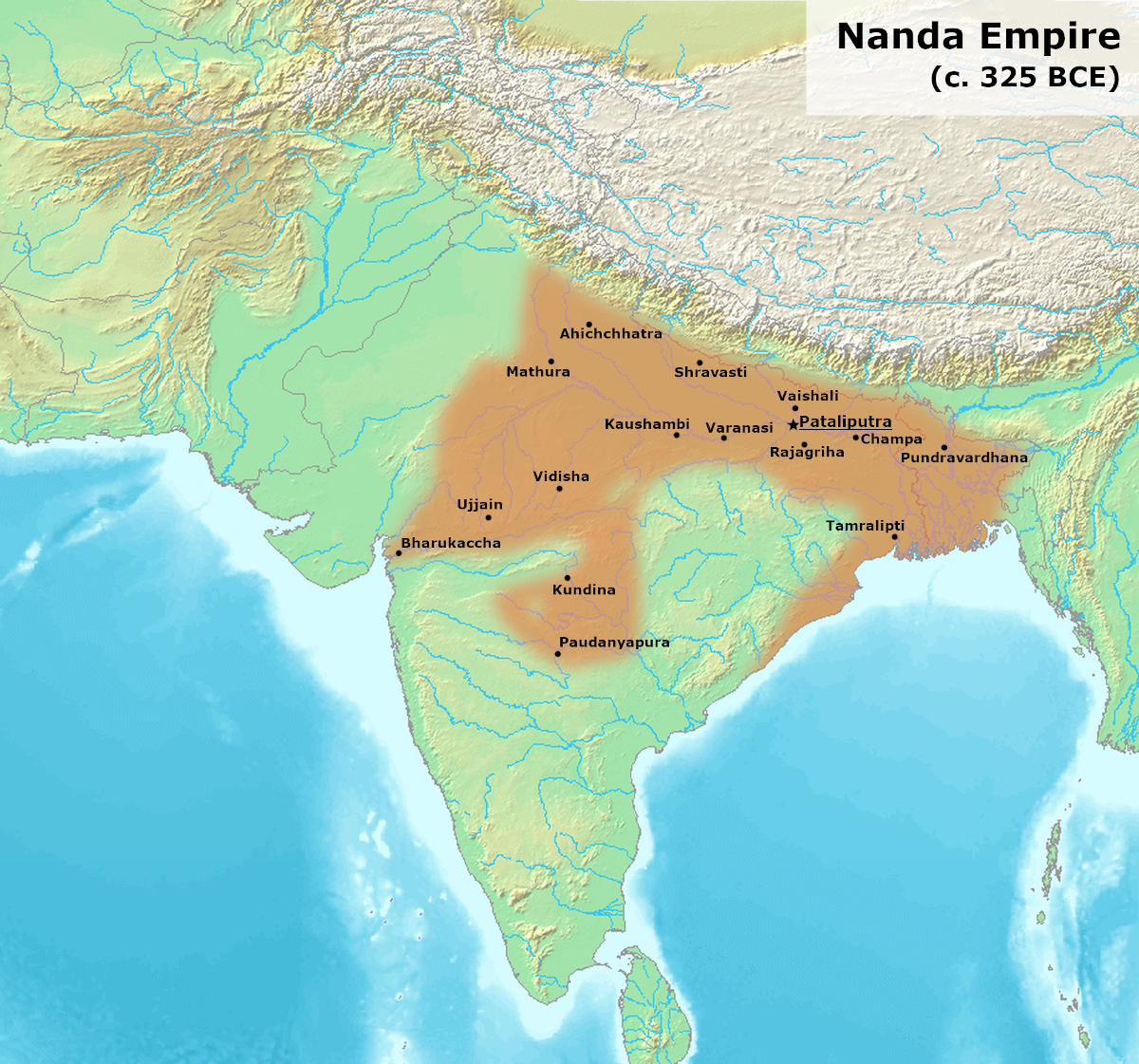
, was the first Emperor of the Nanda Empire
The Nanda dynasty ruled in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent during the fourth century BCE, and possibly during the fifth century BCE. The Nandas overthrew the Shaishunaga dynasty in the Magadha region of eastern India, and expanded ...
of ancient India. The Puranas describe him as a son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
woman. These texts credit him with extensive conquests that expanded the Empire far beyond the Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was rul ...
region. The different Puranas variously give the length of his reign as 28 or 88 years, and state that his eight sons ruled in succession after him.
The Buddhist texts don't mention him, and instead name the first Nanda ruler as robber-turned-king Ugrasena, who was succeeded by his eight brothers, the last of whom was Dhana Nanda.
Reign
 According to the Puranas, Mahapadma or Mahapadma-pati (literally, "lord of the great lotus") was the first Nanda king. He was the son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a
According to the Puranas, Mahapadma or Mahapadma-pati (literally, "lord of the great lotus") was the first Nanda king. He was the son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
woman.
The ''Puranas'' describe him as ''ekarat'' (sole sovereign) and ''sarva-kshatrantaka'' (destroyer of all the ''Kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the co ...
s''). The Kshastriyas (warriors and rulers) said to have been exterminated by Mahapadma include Maithalas, Kasheyas, Ikshvakus, Panchalas, Shurasenas, Kurus, Haihayas, Vitihotras
The Heheya Kingdom (also known as Haihaya, Haiheya, Heiheya _sa.html" ;"title="nowiki/> sa">हैहय was a kingdom ruled by the Yadava people, who claimed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. One of the mo ...
, Kalinga Kalinga may refer to:
Geography, linguistics and/or ethnology
* Kalinga (historical region), a historical region of India
** Kalinga (Mahabharata), an apocryphal kingdom mentioned in classical Indian literature
** Kalinga script, an ancient writin ...
s, and Ashmaka
Ashmaka ( Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts '' Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was located around and between the Godava ...
s.
The '' Matsya Purana'' assigns Mahapadma an incredibly long reign of 88 years, while the ''Vayu Purana
The ''Vayu Purana'' ( sa, वायुपुराण, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas of Hinduism.
''Vayu Purana'' is mentioned in the manuscripts of the Mahabharata and other Hindu texts, which has led scholars to ...
'' mentions the length of his reign as only 28 years. The Puranas further state that Mahapadma's eight sons ruled in succession after him for a total of 12 years, but name only one of these sons: Sukalpa.
Various estimates of the first Nanda emperor's coronation date include:
* Indologist F. E. Pargiter
Frederick Eden Pargiter (1852–18 February 1927) was a British civil servant and Orientalist.
Born in 1852, Pargiter was the second son of Rev. Robert Pargiter. He studied at Taunton Grammar School and Exeter College, Oxford where he passed i ...
: 382 BCE
* Historian R. K. Mookerji: 364 BCE.
* Historian H. C. Raychaudhuri
Hem Chandra Raychaudhuri ( bn, হেম চন্দ্র রায়চৌধুরী) (8 April 1892 – 4 May 1957Raychaudhuri, Hemchandra (1972). ''Political History of Ancient India: From the Accession of Parikshit to the Extinction of ...
: c. 345 BCE.
The beginning of Nanda reign is also assigned as early as 5th century BCE.
Other descriptions of the first Nanda king
* According to the Buddhist texts, the first Nanda king was Ugrasena, not Mahapadma. According to one theory, Ugrasena was probably another name of Mahapadma. ** Unlike the Puranas, which assign mixed royal-Shudra ancestry to Mahapadma, the Buddhist texts describe Ugrasena as of "unknown lineage". According to the ''Mahavamsa-tika'', Ugrasena was a native of the frontier region: he was captured by a gang of robbers, and later became their leader. ** The Greco-Roman sources call the Nanda king ruling at the time ofAlexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
's invasion "Agrammes", which is possibly a corruption of the Sanskrit term "Augraseniya" (literally, "son or descendant of Ugrasena").
** Unlike the Puranas, the Buddhist texts describe the next eight kings as brothers - not sons - of the first Nanda king. Also, according to the Buddhist tradition, the Nandas ruled for a total of 22 years. The last of these kings was Dhana Nanda.
* According to the Jain texts such as '' Parishishtaparvan'' and ''Avashyaka sutra'', which do not mention the name "Mahapadma" either, the Nanda king was the son of a courtesan by a barber. They state that Nanda succeeded Udayin after his death from a rival king. They further state Kalpaka, a non-violent Jain, as his chief-minister, who is believed to have sacrificed his life for peace.
* The Greco-Roman sources suggest that the founder of the Nanda dynasty was a barber, who usurped the throne from the last king of the preceding dynasty. Roman historian Curtius (1st century CE) states that according to Porus, this barber became the former queen's paramour thanks to his attractive looks, treacherously assassinated the then king, usurped the supreme authority by pretending to act as a guardian for the then princes, and later killed the princes. The Nanda king who was the contemporary of Porus and Alexander was the son of this barber.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Nanda, Mahapadma Nanda Empire 4th-century BC Indian monarchs Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown Founding monarchs